The comparison between the human brain and artificial intelligence (so computers) is rooted in their respective capabilities to process and handle information. By examining their processing mechanisms, memory storage, response to environmental stimuli, and interaction with entropy and noise, we can appreciate the fundamental differences and similarities between biological and synthetic systems.
Information Processing
Human Brain: The human brain operates as an incredibly efficient information processor, compressing incoming sensory data from approximately 11 million bits per second to about 50 bits per second during conscious activities like reading or playing piano. This suggests that much of the processing occurs subconsciously and is highly optimized through neural pathways. The brain’s ability to process information is bolstered by its structural complexity, featuring about 100 billion neurons each potentially conducting thousands of operations per second.
Artificial Intelligence: AI systems process information through algorithms and computational models on hardware that can perform billions to trillions of operations per second. Unlike the brain, AI can handle large data streams simultaneously and in parallel without the need for compression to the same extent, as processing power in AI is not limited by biological constraints.
Memory and Learning
Human Brain: Human memory is divided into short-term and long-term storage, with short-term memory capable of holding about 5 to 9 chunks of information at once. Long-term memory, while expansive, is less understood in terms of storage mechanisms and limits. The brain optimizes tasks through practice and habituation, allowing frequent activities to be performed with minimal conscious effort.
Artificial Intelligence: AI uses data storage and retrieval methods that can be adjusted and expanded with hardware upgrades. Machine learning models can modify their processing structures (neural networks) through training, which involves adjusting weights and biases based on error reduction, somewhat analogous to human learning through repetition and correction.
Response to Stimuli and Environmental Interaction
Human Brain: The brain has developed mechanisms to delay reaction to stimuli by about half a second for processing, while maintaining faster reflex pathways for immediate responses. This processing includes significant data compression and filtration to manage the vast amounts of sensory input efficiently.
Artificial Intelligence: AI responses to stimuli are defined by their programming and can be nearly instantaneous without the need for compression. AI systems can be designed to filter noise and manage error through redundancy and error-correction algorithms, continuously improving through updates.
Entropy and Noise
Human Brain: The human brain operates within a “noisy” biological environment, where it continuously adapts to internal and external entropy (disorder). The brain’s management of entropy is not fully understood but is fundamental to its function.
Artificial Intelligence: AI confronts noise through Shannon’s information theory, which guides the design of systems for minimal error transmission and optimal energy expenditure in the presence of noise. AI can leverage these principles to perform operations that may seem to reduce entropy locally, similar to Maxwell’s demon thought experiment, by using information and energy efficiently.
Conclusion
The human brain and artificial intelligence exhibit profound differences in operation and design yet share fundamental goals in information processing, learning, and adaptation to environmental challenges. While the brain is constrained by biological capacities and evolutionary adaptations, AI can be continuously designed, upgraded, and scaled. Understanding both systems enhances our appreciation of human cognitive capabilities and the potential for AI to extend these capabilities.
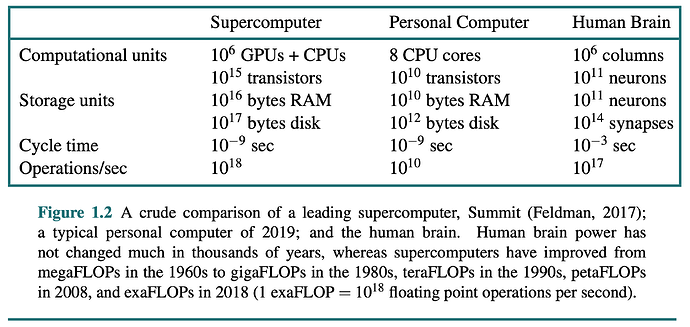
Here is a very excellent technical comparison from the textbook “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 4th Global ed.” This textbook is the golden standard for artificial intelligence education all around the world. It is of course very technical, mathematical, and scientific, but I recommend it to anyone who is thinking about going very deep into AI.